MULTIPLICATION Operator (*) - Excel
Overview
The Multiplication operator (*) in Excel is a useful tool for performing mathematical calculations. This operator allows users to multiply values, cells, or ranges, which makes the creation of complex formulas possible.
Syntax:
=number1 * number2
Here, replace "number1" and "number2" with the specific cells, values, or ranges you want to multiply.
Example: specified cells
In this example, the Multiplication operator is referencing specified cells to do its calculation. Cell C2 equals 11 and cell D2 equals 10, when we multiply them using the Multiplication operator the output is 110.
Example:
=C2 * D2
Example: specified values
In this example, the Multiplication operator is referencing specified values within the cell to do its calculation. The values 5 and 2 are hardcoded into the cell and the final output is 10 when they are multiplied.
Example:
=5 * 2
Example: specified ranges
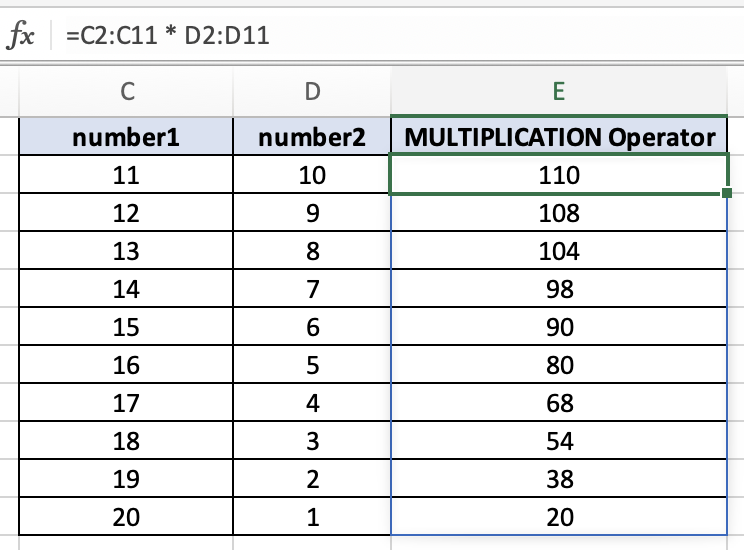
In this example, the Multiplication operator is referencing specified ranges to do its calculation. C2:C11 is the first range and D2:D11 is the second range. When we multiply the ranges using the Multiplication operator, the calculation automatically goes down each row and multiplies it.
Example:
=C2:C11 * D2:D11