LOCATE Function - SQL
Overview
The LOCATE function in SQL returns the position of the first occurrence of a substring within a string. It is useful for finding the position of a substring within a string.
Example:
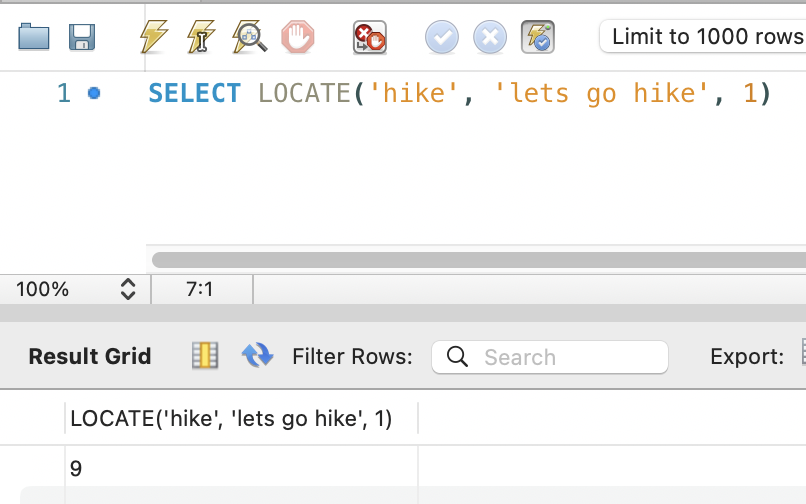
SELECT
LOCATE('hike', 'lets go hike', 1)
Syntax:
SELECT
LOCATE(substring, string, start_position)
substring is the substring you want to find within the string.
string is the string to be searched.
start_position is optional and specifies the position to start the search (default is 1).
Sample Data:
| department_id | first_name |
|---|---|
| 3 | Frank |
| 2 | Jane |
| 3 | Ashley |
| NULL | Glenn |
| 2 | Kelly |
| 1 | Richard |
| 1 | George |
| 5 | Kyle |
| 2 | James |
| 1 | Gustavo |
Example: Hard-coded value
In this example, we are returning the first position of where the ‘hike’ substring is found in the ‘lets go hike’ string, the output is 9.
Example: Query without the WHERE Statement
In this example, we are returning the first position of where the ‘a’ substring is found in the rows of the first_name column. ‘Frank’ is the first name on the list and ‘a’ is in the 3rd position.
Example: Query with the WHERE Statement
In this example, we are returning the first position of where the ‘a’ substring is found in the rows of the first_name column where the department_id equals 1. ‘Richard’ is the first name on the list with this filter and the ‘a’ is in the 5th position.